Using FeatBit REST API
Overview
This guide explains how to get started with the FeatBit REST API. It describes how to create API access tokens, make requests, and evaluate the responses. It introduces common use cases and helps familiarize you with the FeatBit API documentation.
The FeatBit REST API is a programmatic alternative to interacting with the FeatBit user interface (UI). You can use the FeatBit API to perform any action that's available in the flags list, including creating and manipulating flags. For example, the REST API is often used for toggling feature flags, updating segments, and building custom integrations.
Use the FeatBit SDKs to evaluate flags
We do not recommend using the REST API to evaluate feature flags in your application's code. For that, use the FeatBit SDKs. The SDKs include features like caching of flag values and streaming of updates that you won't receive automatically when using the REST API to evaluate flag values. To learn more, read Connect an SDK.
In this guide, you will:
- Set up your request headers to access FeatBit APIs, including creating access tokens
- Read the details of FeatBit resources using the REST API
- Create and update FeatBit resources using the REST API
- Learn common use cases for working with the REST API
Prerequisites
To complete this guide, you must have the following prerequisites:
- Have FeatBit running locally or on a server, read installation.
- Access to a tool for making calls to the REST API. There are many options for this, described below:
Curl
Curl (opens in a new tab) is a common command line tool that you can use to make calls to the REST API. This guide uses curl in its examples. You can run the examples in this guide from your own command line.
Postman
The Postman (opens in a new tab) platform is another option for making calls to the REST API. It offers tooling for setting up, executing, and storing REST requests. You can create a free Postman account and run the examples in this guide from the Postman client.
FeatBit API documentation
The FeatBit API documentation provides examples of each documented request.
FeatBit data hierarchy
An organization can contain one or more projects. A project can contain multiple environments, and feature flags (opens in a new tab) exist within an environment of a project. When you create a new flag, it is created only in that environment. All flag configuration settings are specific to each environment. The changes you make in one environment do not apply to any other environment. If you want to, you can configure the same flag in a unique way for every environment you have.
Many software projects have a test, staging, and production environment within each project. In FeatBit, you can define any environment structure that suits your organization's needs. For example, your mobile team might need android test, android prod, ios test, and ios prod environments in a "Mobile apps" project.
Setting up your headers
Each request you make has the required header information. The header comprises a key/value pair. Many tools for making requests, including curl and Postman, save these headers for you across requests.
If you are using Postman, make sure the Host and Content-Length headers are selected. Those two headers are added automatically if you are using curl or other tools.
Required headers
For all requests, the Authorization header is required. This header authenticates you and checks whether you are authorized to take the requested action on the specified resource. For example, if you request information about a project, but you do not have read access to that project, the response will be an error indicating you don't have sufficient permission.
The value of the Authorization header is an API access token. The access token can be either a personal or service token. In FeatBit, you can create access tokens from the Integrations/Access tokens page. For this guide, you'll need a token with feature flag ManageFeatureFlag permission, so select the ManageFeatureFlag permission (it is selected by default) when you create your token.
To learn more, read Creating API access tokens.
For all requests that include a request body, the API requires a Content-Type header with the value application/json. If the request does not include a body, the API ignores the Content-Type header. This means it is safe to always include the Content-Type header, even when the API doesn't require it.
To include the required headers for your requests in curl, use the -H option:
Example curl
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:5000/api/v1/envs/9d782f01-6ffb-4a7c-83a2-79304d801a46/feature-flags' \ -H 'Authorization: EXAMPLE-API-ACCESS-TOKEN' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json'COPYIn this example, the -X option specifies the type of request, PATCH. The URL specifies the resource that the request is acting on. Each -H option specifies a header that will be included in the request. You must include the -X, request type, URL, and headers each time you use curl to make a request.
Exercise: Reading flag list
Getting the environment Id
As mentioned above, feature flags are environment specific. To list the feature flags of an environment, we need the environment ID (in the feature, it would be possible to call API with environment key).
To get the environment Id:
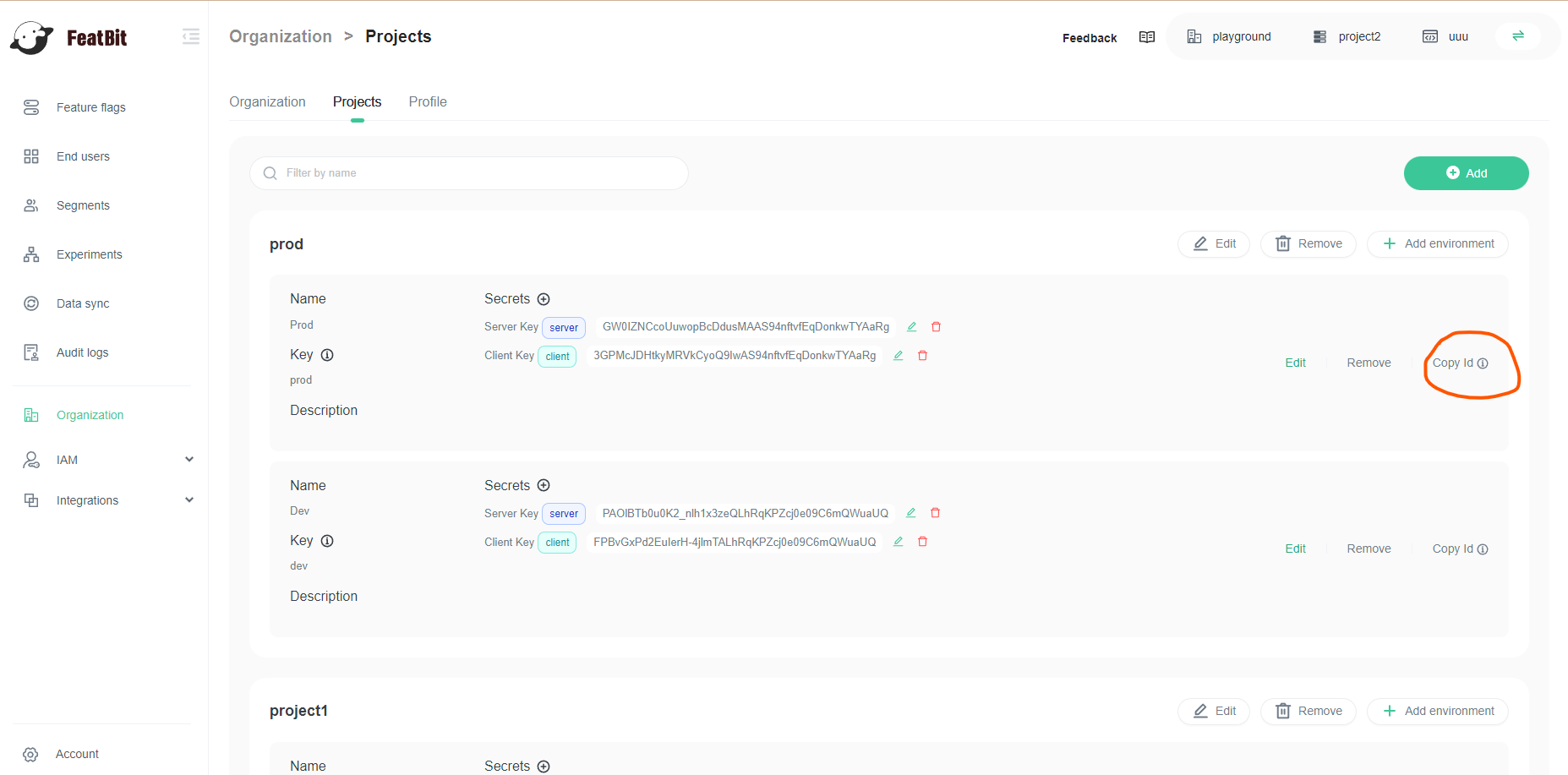
- Go to Organization page and click on Projects tab.
- In the project list, find the project and environment you want to connect to.
- Click on the Copy Id button, the environment id would be copied to clipboard
Call the API
With the environment ID from previous step, make the following call
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:5000/api/v1/envs/[YOUR ENVIRONMENT ID]/feature-flags?pageIndex=0&pageSize=10&isEnabled=' \
-H 'Authorization: EXAMPLE-API-ACCESS-TOKEN'
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'The response to this request is a 200 success code and a JSON object containing everything of the feature flags of that environment. For example:
{
"success": true,
"errors": [],
"data": {
"totalCount": 1,
"items": [
{
"id": "e3d78102-8a67-4698-a744-afcb005e8dfa",
"name": "flag 1",
"description": "",
"key": "flag-1",
"isEnabled": false,
"variationType": "boolean",
"variations": [
{
"id": "838b01b2-d443-4317-b8d3-adb2bed483c0",
"value": "true"
},
{
"id": "0c742a83-0053-4f37-8f34-9ef164c17875",
"value": "false"
}
],
"updatedAt": "2023-03-20T05:44:15.765Z",
"serves": {
"enabledVariations": [
"true"
],
"disabledVariation": "false"
},
"tags": []
}
]
}
}